
Posted on Posted on 5 June 2018 8 November 2018 posted in Categories Announcements, Recent Releases tagged with Tags chemical elements, periodic table, inorganic chemistry, atomic weights, atomic-weight intervals. The atomic weight of bromine has changed from 79.904(1) to the interval 79.901, 79.907, germanium from 72.63(1) to 72.630(8), indium from 114.818(3) to 114.818(1), magnesium from 24.3050(6) to the interval 24.304, 24.307, and mercury from 200.59(2) to 200.592(3). Atomic weight is the average mass of atoms of an element, calculated using the relative abundance of isotopes in a naturally-occurring element. It is the weighted average of the masses of naturally-occurring isotopes. What Is It Based On? Prior to 1961, a unit of atomic weight was based on 1/16th (0.0625) of the weight of an oxygen atom. Atomic weight definition is - the mass of one atom of an element; specifically: the average mass of an atom of an element as it occurs in nature that is expressed in atomic mass units. For chemistry students and teachers: The tabular chart on the right is arranged by Atomic mass (weight). The lightest chemical element is Hydrogen and the heaviest is Hassium. The unity for atomic mass is gram per mol. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system.
Standard atomic weights are CIAAW recommended values for atomic weights applicable to all normal materials.Since 1902, the Commission regularly publishes critical evaluation of atomic weights of elements and below is the most recent definitive table of the standard atomic weights.
| Z | Symbol | Element | Standard Atomic Weight | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | hydrogen | [1.007 84, 1.008 11] | m |
| 2 | He | helium | 4.002 602(2) | |
| 3 | Li | lithium | [6.938, 6.997] | m |
| 4 | Be | beryllium | 9.012 1831(5) | |
| 5 | B | boron | [10.806, 10.821] | m |
| 6 | C | carbon | [12.0096, 12.0116] | |
| 7 | N | nitrogen | [14.006 43, 14.007 28] | m |
| 8 | O | oxygen | [15.999 03, 15.999 77] | m |
| 9 | F | fluorine | 18.998 403 163(6) | |
| 10 | Ne | neon | 20.1797(6) | |
| 11 | Na | sodium | 22.989 769 28(2) | |
| 12 | Mg | magnesium | [24.304, 24.307] | |
| 13 | Al | aluminium | 26.981 5384(3) | |
| 14 | Si | silicon | [28.084, 28.086] | |
| 15 | P | phosphorus | 30.973 761 998(5) | |
| 16 | S | sulfur | [32.059, 32.076] | |
| 17 | Cl | chlorine | [35.446, 35.457] | m |
| 18 | Ar | argon | [39.792, 39.963] | |
| 19 | K | potassium | 39.0983(1) | |
| 20 | Ca | calcium | 40.078(4) | g |
| 21 | Sc | scandium | 44.955 908(5) | |
| 22 | Ti | titanium | 47.867(1) | |
| 23 | V | vanadium | 50.9415(1) | |
| 24 | Cr | chromium | 51.9961(6) | |
| 25 | Mn | manganese | 54.938 043(2) | |
| 26 | Fe | iron | 55.845(2) | |
| 27 | Co | cobalt | 58.933 194(3) | |
| 28 | Ni | nickel | 58.6934(4) | r |
| 29 | Cu | copper | 63.546(3) | r |
| 30 | Zn | zinc | 65.38(2) | r |
| 31 | Ga | gallium | 69.723(1) | |
| 32 | Ge | germanium | 72.630(8) | |
| 33 | As | arsenic | 74.921 595(6) | |
| 34 | Se | selenium | 78.971(8) | r |
| 35 | Br | bromine | [79.901, 79.907] | |
| 36 | Kr | krypton | 83.798(2) | |
| 37 | Rb | rubidium | 85.4678(3) | g |
| 38 | Sr | strontium | 87.62(1) | |
| 39 | Y | yttrium | 88.905 84(1) | |
| 40 | Zr | zirconium | 91.224(2) | g |
| 41 | Nb | niobium | 92.906 37(1) | |
| 42 | Mo | molybdenum | 95.95(1) | g |
| 43 | Tc | technetium | — | |
| 44 | Ru | ruthenium | 101.07(2) | g |
| 45 | Rh | rhodium | 102.905 49(2) | |
| 46 | Pd | palladium | 106.42(1) | g |
| 47 | Ag | silver | 107.8682(2) | g |
| 48 | Cd | cadmium | 112.414(4) | g |
| 49 | In | indium | 114.818(1) | |
| 50 | Sn | tin | 118.710(7) | g |
| 51 | Sb | antimony | 121.760(1) | g |
| 52 | Te | tellurium | 127.60(3) | g |
| 53 | I | iodine | 126.904 47(3) | |
| 54 | Xe | xenon | 131.293(6) | |
| 55 | Cs | caesium | 132.905 451 96(6) | |
| 56 | Ba | barium | 137.327(7) | |
| 57 | La | lanthanum | 138.905 47(7) | g |
| 58 | Ce | cerium | 140.116(1) | g |
| 59 | Pr | praseodymium | 140.907 66(1) | |
| 60 | Nd | neodymium | 144.242(3) | g |
| 61 | Pm | promethium | — | |
| 62 | Sm | samarium | 150.36(2) | g |
| 63 | Eu | europium | 151.964(1) | g |
| 64 | Gd | gadolinium | 157.25(3) | g |
| 65 | Tb | terbium | 158.925 354(8) | |
| 66 | Dy | dysprosium | 162.500(1) | g |
| 67 | Ho | holmium | 164.930 328(7) | |
| 68 | Er | erbium | 167.259(3) | g |
| 69 | Tm | thulium | 168.934 218(6) | |
| 70 | Yb | ytterbium | 173.045(10) | g |
| 71 | Lu | lutetium | 174.9668(1) | g |
| 72 | Hf | hafnium | 178.486(6) | g |
| 73 | Ta | tantalum | 180.947 88(2) | |
| 74 | W | tungsten | 183.84(1) | |
| 75 | Re | rhenium | 186.207(1) | |
| 76 | Os | osmium | 190.23(3) | g |
| 77 | Ir | iridium | 192.217(2) | |
| 78 | Pt | platinum | 195.084(9) | |
| 79 | Au | gold | 196.966 570(4) | |
| 80 | Hg | mercury | 200.592(3) | |
| 81 | Tl | thallium | [204.382, 204.385] | |
| 82 | Pb | lead | 207.2(1) | |
| 83 | Bi | bismuth | 208.980 40(1) | |
| 84 | Po | polonium | — | |
| 85 | At | astatine | — | |
| 86 | Rn | radon | — | |
| 87 | Fr | francium | — | |
| 88 | Ra | radium | — | |
| 89 | Ac | actinium | — | |
| 90 | Th | thorium | 232.0377(4) | |
| 91 | Pa | protactinium | 231.035 88(1) | |
| 92 | U | uranium | 238.028 91(3) | |
| 93 | Np | neptunium | — | |
| 94 | Pu | plutonium | — | |
| 95 | Am | americium | — | |
| 96 | Cm | curium | — | |
| 97 | Bk | berkelium | — | |
| 98 | Cf | californium | — | |
| 99 | Es | einsteinium | — | |
| 100 | Fm | fermium | — | |
| 101 | Md | mendelevium | — | |
| 102 | No | nobelium | — | |
| 103 | Lr | lawrencium | — | |
| 104 | Rf | rutherfordium | — | |
| 105 | Db | dubnium | — | |
| 106 | Sg | seaborgium | — | |
| 107 | Bh | bohrium | — | |
| 108 | Hs | hassium | — | |
| 109 | Mt | meitnerium | — | |
| 110 | Ds | darmstadtium | — | |
| 111 | Rg | roentgenium | — | |
| 112 | Cn | copernicium | — | |
| 113 | Nh | nihonium | — | |
| 114 | Fl | flerovium | — | |
| 115 | Mc | moscovium | — | |
| 116 | Lv | livermorium | — | |
| 117 | Ts | tennessine | — | |
| 118 | Og | oganesson | — | |
| Z | Symbol | Element | Standard Atomic Weight | Notes |
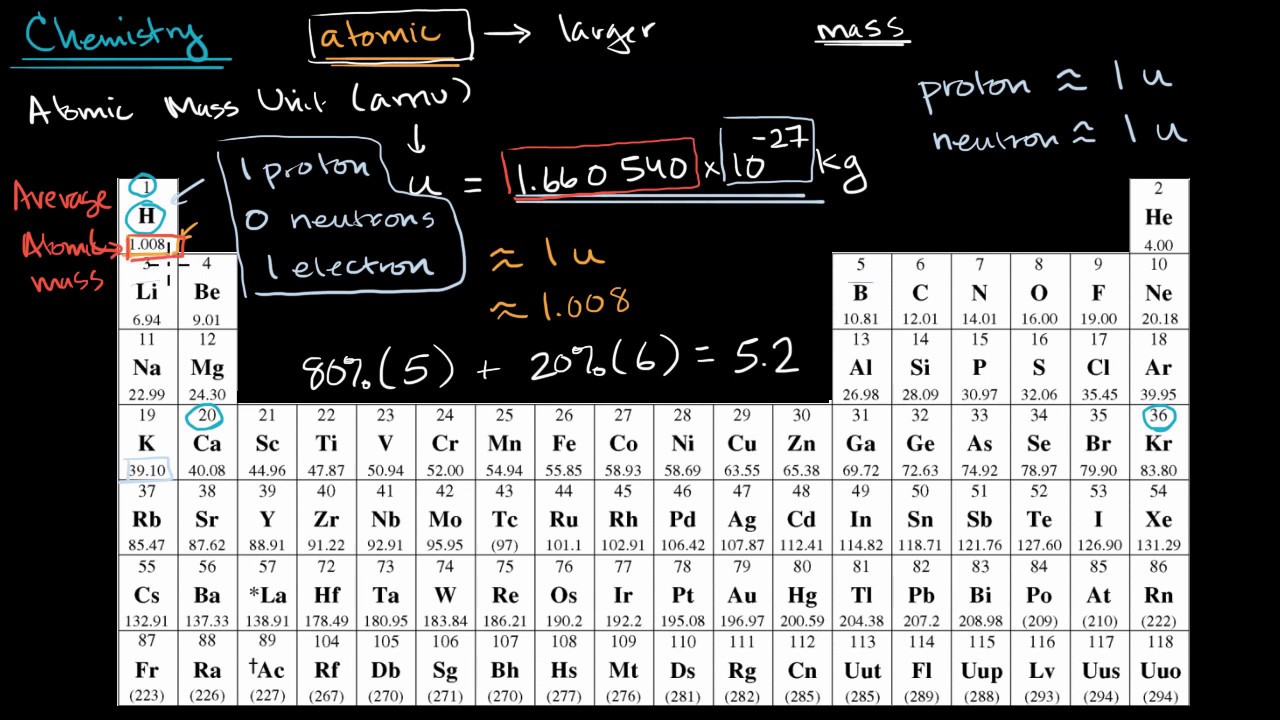
Posted on Posted on 5 June 2018 8 November 2018 posted in Categories Announcements, Recent Releases tagged with Tags chemical elements, periodic table, inorganic chemistry, atomic weights, atomic-weight intervals. The atomic weight of bromine has changed from 79.904(1) to the interval 79.901, 79.907, germanium from 72.63(1) to 72.630(8), indium from 114.818(3) to 114.818(1), magnesium from 24.3050(6) to the interval 24.304, 24.307, and mercury from 200.59(2) to 200.592(3). Atomic weight is the average mass of atoms of an element, calculated using the relative abundance of isotopes in a naturally-occurring element. It is the weighted average of the masses of naturally-occurring isotopes. What Is It Based On? Prior to 1961, a unit of atomic weight was based on 1/16th (0.0625) of the weight of an oxygen atom. Atomic weight definition is - the mass of one atom of an element; specifically: the average mass of an atom of an element as it occurs in nature that is expressed in atomic mass units. For chemistry students and teachers: The tabular chart on the right is arranged by Atomic mass (weight). The lightest chemical element is Hydrogen and the heaviest is Hassium. The unity for atomic mass is gram per mol. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system.
Standard atomic weights are CIAAW recommended values for atomic weights applicable to all normal materials.Since 1902, the Commission regularly publishes critical evaluation of atomic weights of elements and below is the most recent definitive table of the standard atomic weights.
| Z | Symbol | Element | Standard Atomic Weight | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | hydrogen | [1.007 84, 1.008 11] | m |
| 2 | He | helium | 4.002 602(2) | |
| 3 | Li | lithium | [6.938, 6.997] | m |
| 4 | Be | beryllium | 9.012 1831(5) | |
| 5 | B | boron | [10.806, 10.821] | m |
| 6 | C | carbon | [12.0096, 12.0116] | |
| 7 | N | nitrogen | [14.006 43, 14.007 28] | m |
| 8 | O | oxygen | [15.999 03, 15.999 77] | m |
| 9 | F | fluorine | 18.998 403 163(6) | |
| 10 | Ne | neon | 20.1797(6) | |
| 11 | Na | sodium | 22.989 769 28(2) | |
| 12 | Mg | magnesium | [24.304, 24.307] | |
| 13 | Al | aluminium | 26.981 5384(3) | |
| 14 | Si | silicon | [28.084, 28.086] | |
| 15 | P | phosphorus | 30.973 761 998(5) | |
| 16 | S | sulfur | [32.059, 32.076] | |
| 17 | Cl | chlorine | [35.446, 35.457] | m |
| 18 | Ar | argon | [39.792, 39.963] | |
| 19 | K | potassium | 39.0983(1) | |
| 20 | Ca | calcium | 40.078(4) | g |
| 21 | Sc | scandium | 44.955 908(5) | |
| 22 | Ti | titanium | 47.867(1) | |
| 23 | V | vanadium | 50.9415(1) | |
| 24 | Cr | chromium | 51.9961(6) | |
| 25 | Mn | manganese | 54.938 043(2) | |
| 26 | Fe | iron | 55.845(2) | |
| 27 | Co | cobalt | 58.933 194(3) | |
| 28 | Ni | nickel | 58.6934(4) | r |
| 29 | Cu | copper | 63.546(3) | r |
| 30 | Zn | zinc | 65.38(2) | r |
| 31 | Ga | gallium | 69.723(1) | |
| 32 | Ge | germanium | 72.630(8) | |
| 33 | As | arsenic | 74.921 595(6) | |
| 34 | Se | selenium | 78.971(8) | r |
| 35 | Br | bromine | [79.901, 79.907] | |
| 36 | Kr | krypton | 83.798(2) | |
| 37 | Rb | rubidium | 85.4678(3) | g |
| 38 | Sr | strontium | 87.62(1) | |
| 39 | Y | yttrium | 88.905 84(1) | |
| 40 | Zr | zirconium | 91.224(2) | g |
| 41 | Nb | niobium | 92.906 37(1) | |
| 42 | Mo | molybdenum | 95.95(1) | g |
| 43 | Tc | technetium | — | |
| 44 | Ru | ruthenium | 101.07(2) | g |
| 45 | Rh | rhodium | 102.905 49(2) | |
| 46 | Pd | palladium | 106.42(1) | g |
| 47 | Ag | silver | 107.8682(2) | g |
| 48 | Cd | cadmium | 112.414(4) | g |
| 49 | In | indium | 114.818(1) | |
| 50 | Sn | tin | 118.710(7) | g |
| 51 | Sb | antimony | 121.760(1) | g |
| 52 | Te | tellurium | 127.60(3) | g |
| 53 | I | iodine | 126.904 47(3) | |
| 54 | Xe | xenon | 131.293(6) | |
| 55 | Cs | caesium | 132.905 451 96(6) | |
| 56 | Ba | barium | 137.327(7) | |
| 57 | La | lanthanum | 138.905 47(7) | g |
| 58 | Ce | cerium | 140.116(1) | g |
| 59 | Pr | praseodymium | 140.907 66(1) | |
| 60 | Nd | neodymium | 144.242(3) | g |
| 61 | Pm | promethium | — | |
| 62 | Sm | samarium | 150.36(2) | g |
| 63 | Eu | europium | 151.964(1) | g |
| 64 | Gd | gadolinium | 157.25(3) | g |
| 65 | Tb | terbium | 158.925 354(8) | |
| 66 | Dy | dysprosium | 162.500(1) | g |
| 67 | Ho | holmium | 164.930 328(7) | |
| 68 | Er | erbium | 167.259(3) | g |
| 69 | Tm | thulium | 168.934 218(6) | |
| 70 | Yb | ytterbium | 173.045(10) | g |
| 71 | Lu | lutetium | 174.9668(1) | g |
| 72 | Hf | hafnium | 178.486(6) | g |
| 73 | Ta | tantalum | 180.947 88(2) | |
| 74 | W | tungsten | 183.84(1) | |
| 75 | Re | rhenium | 186.207(1) | |
| 76 | Os | osmium | 190.23(3) | g |
| 77 | Ir | iridium | 192.217(2) | |
| 78 | Pt | platinum | 195.084(9) | |
| 79 | Au | gold | 196.966 570(4) | |
| 80 | Hg | mercury | 200.592(3) | |
| 81 | Tl | thallium | [204.382, 204.385] | |
| 82 | Pb | lead | 207.2(1) | |
| 83 | Bi | bismuth | 208.980 40(1) | |
| 84 | Po | polonium | — | |
| 85 | At | astatine | — | |
| 86 | Rn | radon | — | |
| 87 | Fr | francium | — | |
| 88 | Ra | radium | — | |
| 89 | Ac | actinium | — | |
| 90 | Th | thorium | 232.0377(4) | |
| 91 | Pa | protactinium | 231.035 88(1) | |
| 92 | U | uranium | 238.028 91(3) | |
| 93 | Np | neptunium | — | |
| 94 | Pu | plutonium | — | |
| 95 | Am | americium | — | |
| 96 | Cm | curium | — | |
| 97 | Bk | berkelium | — | |
| 98 | Cf | californium | — | |
| 99 | Es | einsteinium | — | |
| 100 | Fm | fermium | — | |
| 101 | Md | mendelevium | — | |
| 102 | No | nobelium | — | |
| 103 | Lr | lawrencium | — | |
| 104 | Rf | rutherfordium | — | |
| 105 | Db | dubnium | — | |
| 106 | Sg | seaborgium | — | |
| 107 | Bh | bohrium | — | |
| 108 | Hs | hassium | — | |
| 109 | Mt | meitnerium | — | |
| 110 | Ds | darmstadtium | — | |
| 111 | Rg | roentgenium | — | |
| 112 | Cn | copernicium | — | |
| 113 | Nh | nihonium | — | |
| 114 | Fl | flerovium | — | |
| 115 | Mc | moscovium | — | |
| 116 | Lv | livermorium | — | |
| 117 | Ts | tennessine | — | |
| 118 | Og | oganesson | — | |
| Z | Symbol | Element | Standard Atomic Weight | Notes |
FootnotesBack to Top
g Geological materials are known in which the element has an isotopic composition outside the limits for normal material. The difference between the atomic weight of the element in such materials and that given in the table may exceed the stated uncertainty.
m Modified isotopic compositions may be found in commercially available material because the material has been subjected to an undisclosed or inadvertent isotopic fractionation. Substantial deviations in atomic weight of the element from that given in the table can occur.
r Range in isotopic composition of normal terrestrial material prevents a more precise standard atomic weight being given; the tabulated atomic-weight value and uncertainty should be applicable to normal materials.
Citation Shift down arrow.
The most recent Standard Atomic Weights are presented in this Table and they are based on the 'Atomic Weights 2013' report and on the subsequent revisions that were made by the CIAAW in 2015, in 2017, and in 2019.
This Table can be cited as follows:
CIAAW. Atomic weights of the elements 2019. Available online at www.ciaaw.org.
There are three broad groups of elements depending on what is the main cause of the uncertainty of their standard atomic weights:
(1) well-documented natural variations of isotopic abundances,
(2) our ability to determine the isotopic abundances, and
(3) our ability to precisely determine the atomic masses of the isotopes.
Elements in the first category are distinguished by an interval standard atomic weight. Online garage sale.
Atomic Weight Definition
The reported uncertainties of the standard atomic weights are such that the atomic-weight values of normal materials are expected to lie in the given interval with great certitude.For instance, the standard atomic weight of argon, [39.792, 39.963], indicates that atomic-weight values of argon in normal materials are expected to be from 39.792 to 39.963. For iridium, the standard atomic weight 192.217(2) indicates that atomic-weight values of iridium in normal materials are expected to be from 192.215 to 192.219.
For more information on the interpretation of the uncertainty please consult the recent IUPAC Technical Report by Possolo et al.
